Galeria
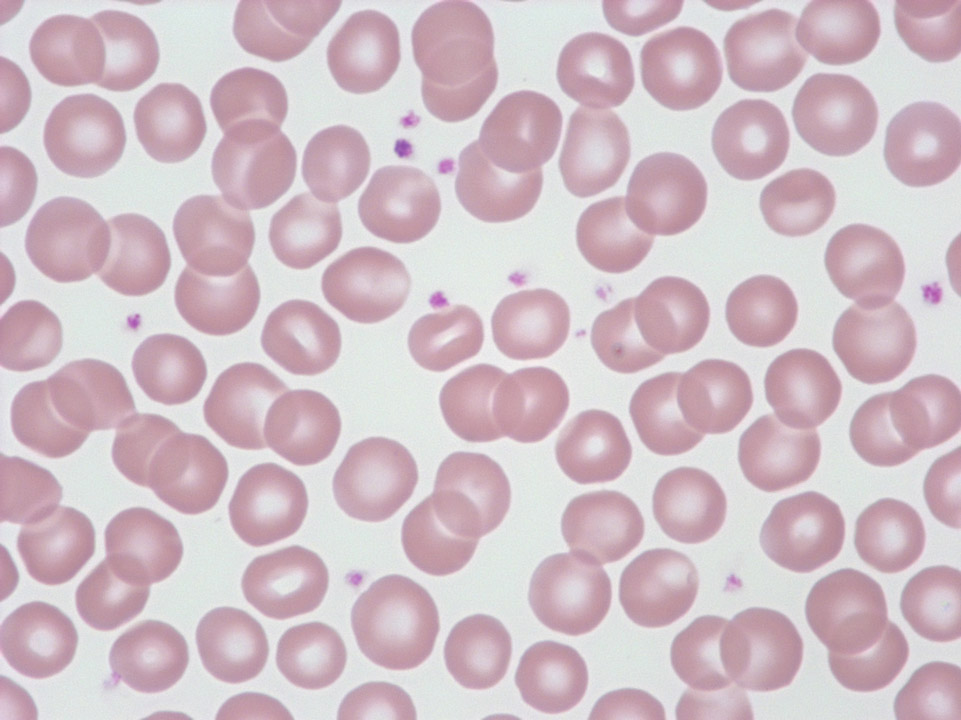
It is of utmost importance to always report a correct value for the platelet concentration. When detecting thrombocytopenia the laboratory should therefore double-check that it is not due to platelet aggregates (->) (pseudo-thrombocytopenia). In a haematology analyser they are usually automatically identified and flagged. In a blood film they are mostly located at the feather edge or the lateral edges.
<p>It is of utmost importance to always report a correct value for the platelet concentration. When detecting thrombocytopenia the laboratory should therefore double-check that it is not due to platelet aggregates (->) (pseudo-thrombocytopenia). In a haematology analyser they are usually automatically identified and flagged. In a blood film they are mostly located at the feather edge or the lateral edges.</p>
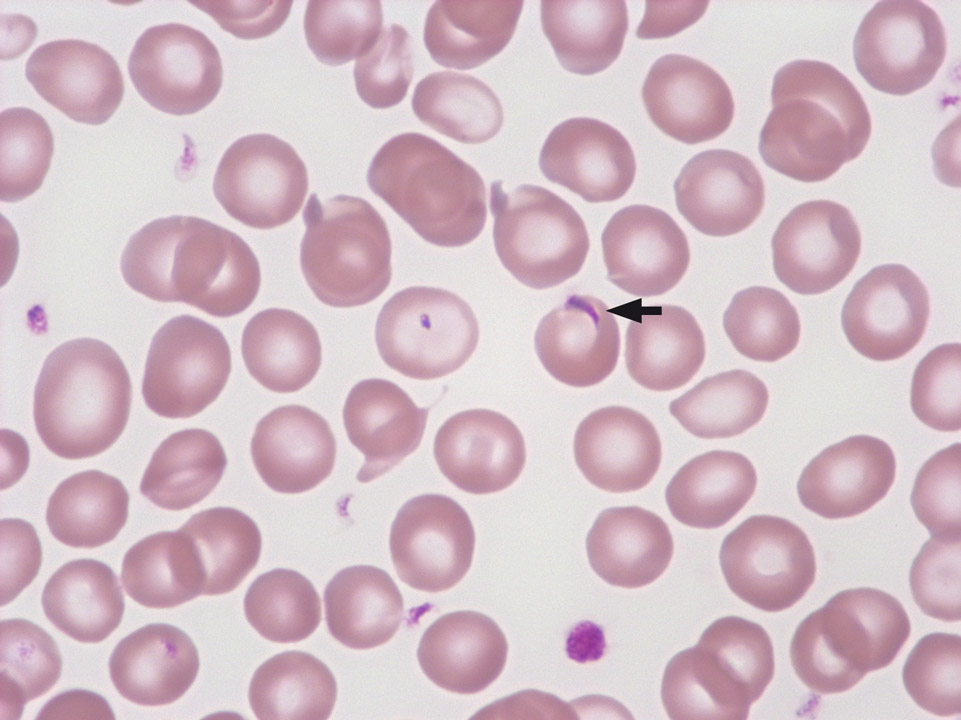
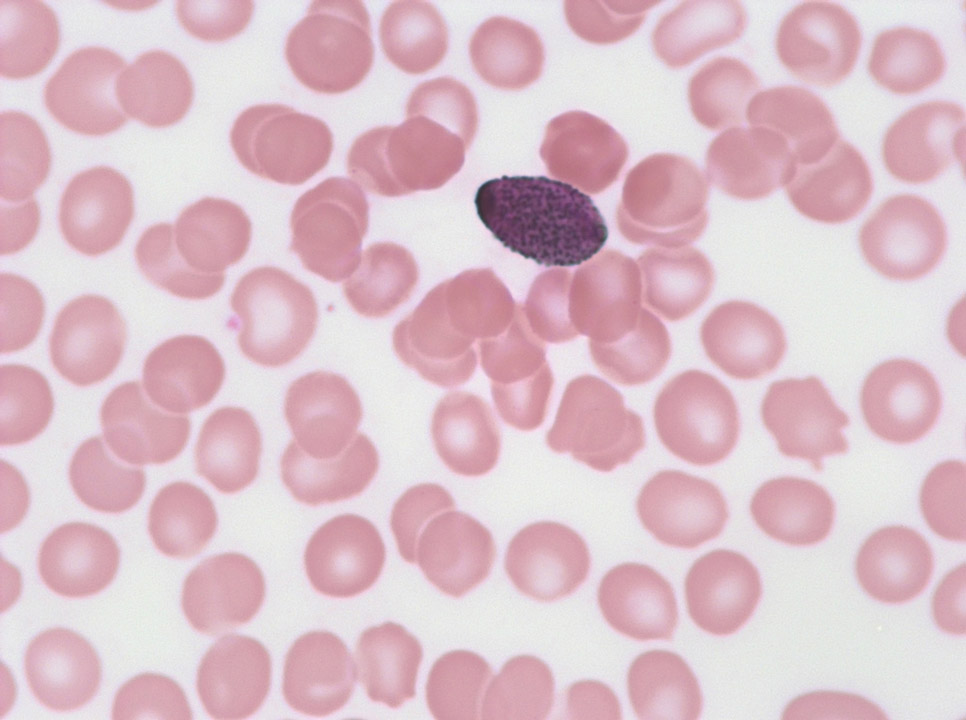
Platelets can lie on top of red blood cells, and look very much like Plasmodia. (By turning the micrometre screw, one will realize quite easily that the object is on top of the red blood cell and not inside it, as it would be with Plasmodia.)
<p>Platelets can lie on top of red blood cells, and look very much like Plasmodia. (By turning the micrometre screw, one will realize quite easily that the object is on top of the red blood cell and not inside it, as it would be with Plasmodia.)</p>
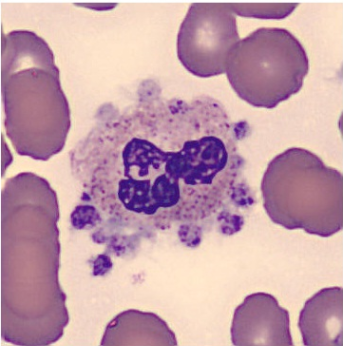
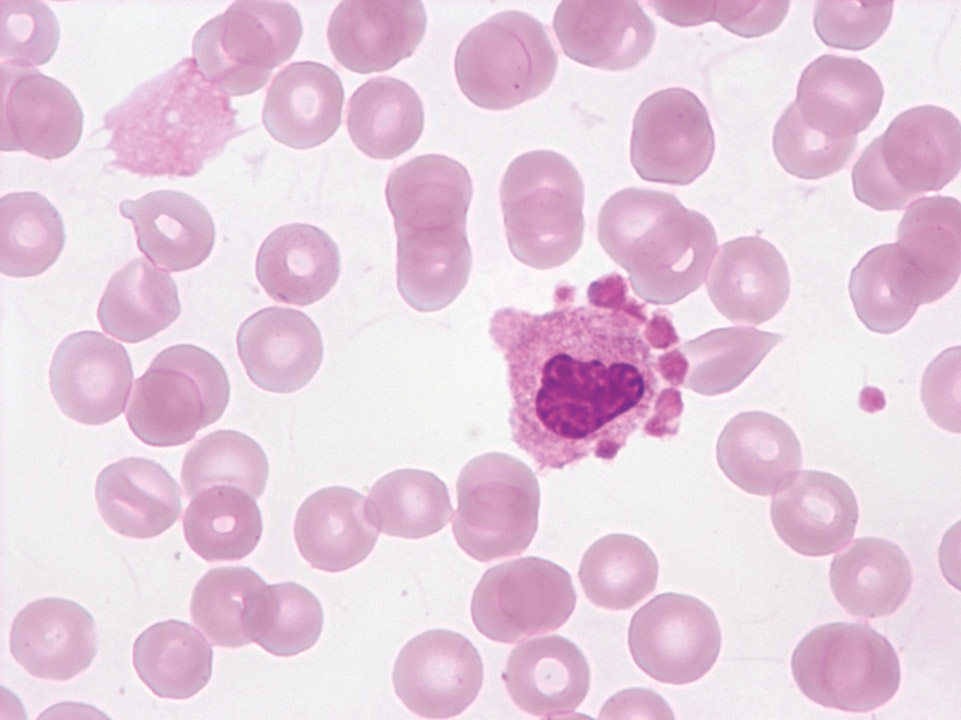
Platelet satellitosis is a rare phenomenon of platelets aggregating around polymorphonuclear white blood cells. It appears to be induced or enhanced by the presence of EDTA, a commonly used anticoagulant, and is not associated with any definite disease process.
<p>Platelet satellitosis is a rare phenomenon of platelets aggregating around polymorphonuclear white blood cells. It appears to be induced or enhanced by the presence of EDTA, a commonly used anticoagulant, and is not associated with any definite disease process.</p>
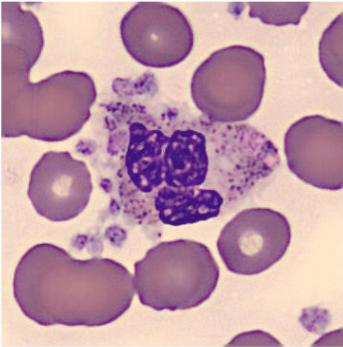
Platelet satellitosis is a rare phenomenon of platelets aggregating around polymorphonuclear white blood cells. It appears to be induced or enhanced by the presence of EDTA, a commonly used anticoagulant, and is not associated with any definite disease process.
<p>Platelet satellitosis is a rare phenomenon of platelets aggregating around polymorphonuclear white blood cells. It appears to be induced or enhanced by the presence of EDTA, a commonly used anticoagulant, and is not associated with any definite disease process.</p>
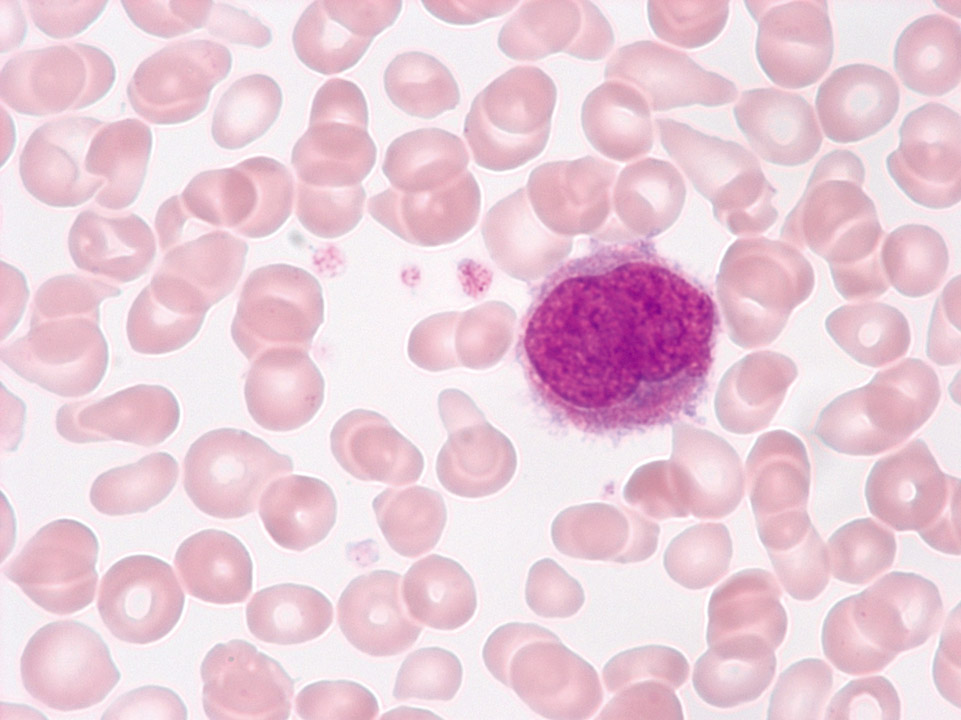
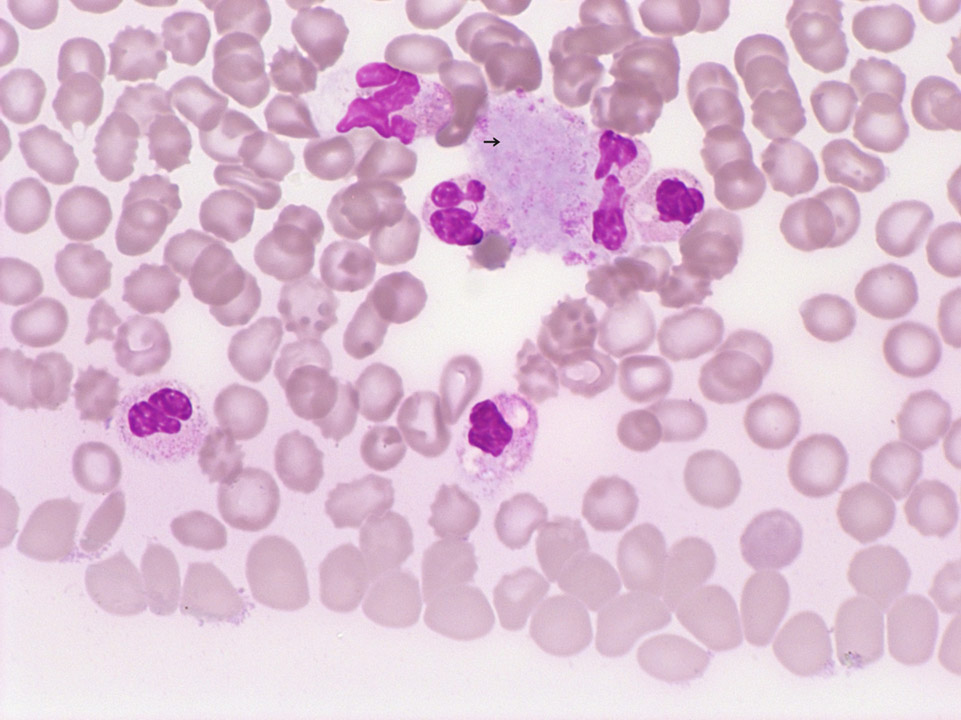
In primary myelofibrosis (PMF, also called chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, CIMF) nuclei of megakaryocytes can be detected in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) and rarely, like here, small megakaryocytes. Both derive from extramedullary haematopoiesis.
<p>In primary myelofibrosis (PMF, also called chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, CIMF) nuclei of megakaryocytes can be detected in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) and rarely, like here, small megakaryocytes. Both derive from extramedullary haematopoiesis.</p>
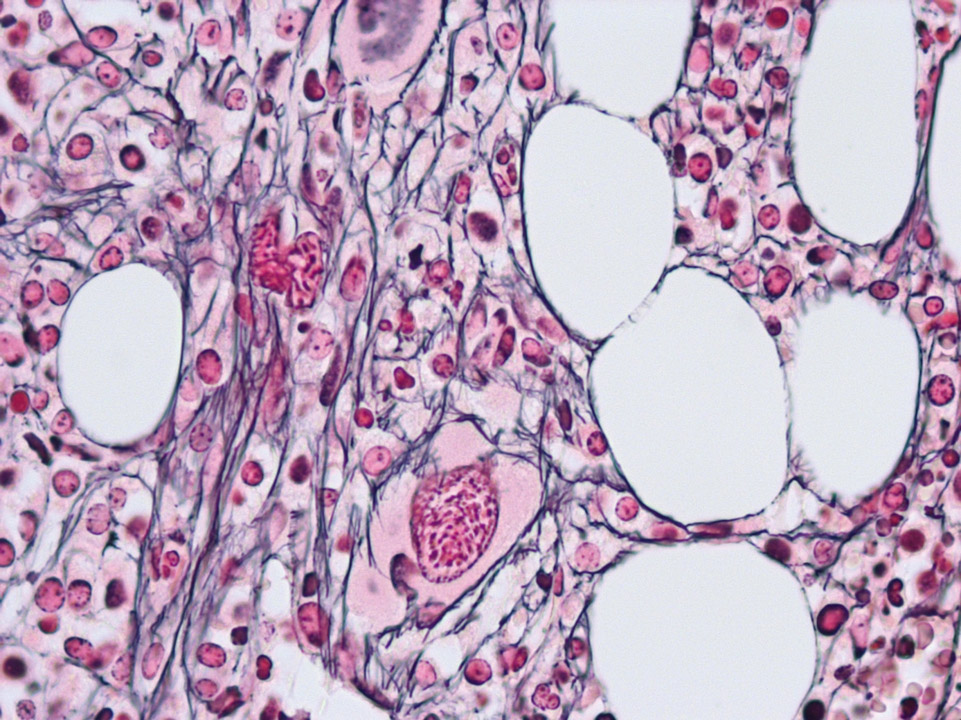
In the bone marrow histology the reticular fibres in PMF (alo called CIMF) can be identified by their black colour (Gomori stain).
<p>In the bone marrow histology the reticular fibres in PMF (alo called CIMF) can be identified by their black colour (Gomori stain). </p>